RADIATION PROTECTION IN FIELD OF RADIOLOGY
Citation: Rizvi. M. (2023, October 03). RADIATION PROTECTION IN FIELD OF RADIOLOGY. (J. Siddiqui, Ed.) Little Lady House, 01(01), 03.
Radiology is a vital discipline of medicine that provides medical practitioners with valuable diagnostic tools. It is hard to overestimate the value of radiation shielding. This article will go over the many aspects of radiation protection in field of radiology. The significance, methodologies, and critical trials to ensure patient and paramedic safety will be presented.
Read this informative article: Top Heart Surgeons in the USA
RADIATION PROTECTION IN MEDICAL RADIOGRAPHY
In hospitals, X-rays and other kinds of medical radiography are routinely used diagnostic tools. Several strategies are used in healthcare facilities to ensure radiation safety during radiography. These include properly aligning the patients, adjusting the settings on the X-ray apparatus to reduce contact, and utilizing lead overalls, thyroid protections, and lead curtains to shield the paramedics through stray energy.
ALARA
ALARA, or “As Low as Reasonably Achievable,” is a radiation shielding principle. It emphasizes limiting radiation exposure to the lowest possible level. ALARA controls radiological safety measures and ensures that doses are maintained as low as possible to safeguard patients and health staff.
RADIATION PROTECTION DEVICES
Radiation defence gear practice is critical for limiting energy interaction. Lead overalls, lead ramparts, gonadal shielding, glasses, and thyroid shields are the furthermost commonly used kits. They are used to effectively prevent ionizing radiation. These devices are critical for protecting healthcare practitioners from the stochastic and predictable effects of radiation.
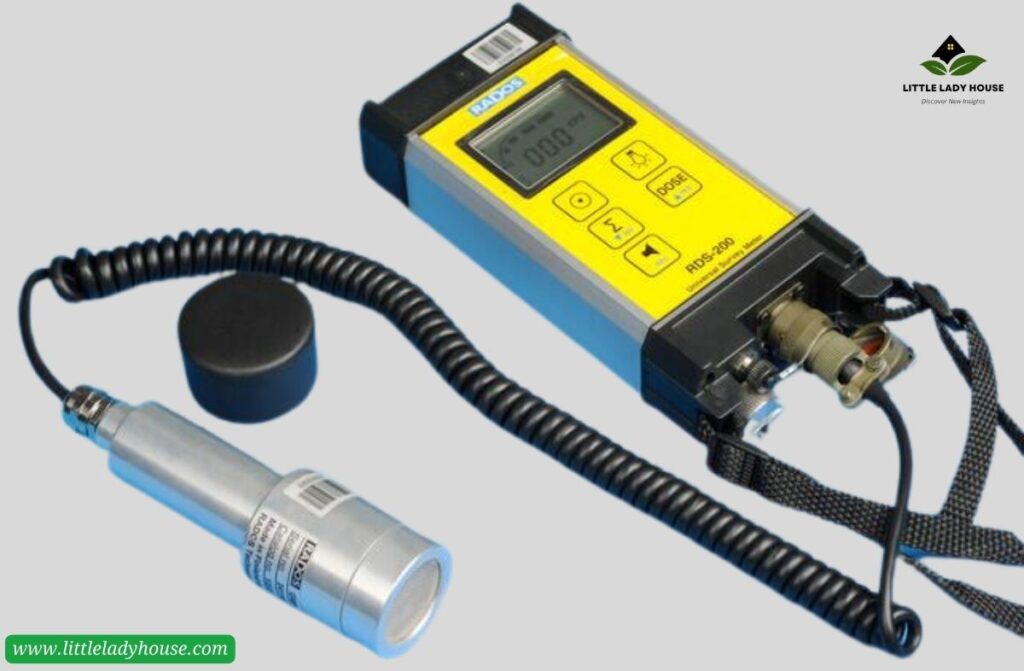
MEASUREMENT DEVICES FOR RADIATION
Survey meters, dosimeters, scintillation detectors, and Geiger-Muller counters are used to determine radiation points. TLDs, Ionisation Chambers, and Personal Radiation Detectors are used to measure individual exposure. Sensors of neutron detectors and spectrometers enable more accurate analysis. Contamination monitors also search for radioactive pollutants.
RADIATION HARMFUL EFFECTS
Contact with ionizing radiation increases the risk of acquiring radiation illnesses such as:
• Cancer
• Cataract
• Cellular harm
• Birth anomalies
• Skin problems
• Long-term health problems
PROTECTION AGAINST DANGEROUS CONTAMINATION
Improper ionizing energy management might have undesirable consequences. The notions of optimisation along with ALARA fight against dangerous energy. The aim of healthcare practitioners is to obtain essential diagnostic data with as little radiation exposure as possible. To decrease energy exposure, techniques such as filtering and collimation are applied.
You should read this informative article: Vapor vs. Smoke: The Evolving World of Inhalation
LEAD TENDER FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Due to high atomic number and compactness of lead, it is an essential substance for radiation protection. It is cast-off to construct protective walls, doors, separators, glasses, shutters, and barriers. Lead is also used to make lead overalls, gonadal protection, and thyroid defending apparels. This thick, hefty material is essential for radiation protection because it absorbs and inhibits ionizing radiation efficiently.
RADIATION PROTECTION DURING X-RAYS
The basis of diagnostic radiology is the X-ray. Healthcare personnel adheres to the ALARA ethics by employing the proper collimation, beam filtering, and exposure. Lesser radiation doses and shielding are used to protect pediatric patients. Because they are more prone to radiation.
RADIATION PROTECTION DURING CT SCANS
CT scans are a useful diagnostic tool, they need larger radiation dose than X-rays. Modern technology is made to reduce unwanted radiation during CT scans. Procedures to lessen radiation experience includes the collimation, filtration, tube current modulation and automated exposure control. Moreover, use of thyroid shields and lead aprons also play role.
Here is another article: Radiation protection in radiology
RADIATION PROTECTION DURING ANGIOGRAPHY
A specialized radiological technique called angiography is used to identify vascular disorders and see blood vessels. Contrast agent injections are often used, which rises radiation contact. Lead aprons, lead glasses and shields are used during angiography to protect from excess radiation. Radiation dosages are closely monitored.
RADIATION PROTECTION DURING NUCLEAR MEDICINE SCANS
Radioactive isotopes are used in nuclear medicine scans to identify and treat various medical disorders. In nuclear medicine, ensuring radiation protection is crucial. To reduce radiation exposure, healthcare personnel use lead aprons and maintain a distance from the radioactivity basis.
CONCLUSION
Radiation protection in field of radiology is vital for the well-being and protection of both patients and staffs. Strict precautionary precautions must be taken because radiation’s stochastic and deterministic effects can have catastrophic results. Components of minimizing radiation exposure are the usage of collimation, filtration, usage of lead, and radiation shielding devices. Radiology may continue to offer vital diagnostic data while minimizing the hazards related to ionizing radiation by continuously focusing on safety and optimization.
To keep updated with the latest health-related posts, click here.